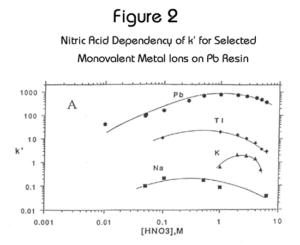
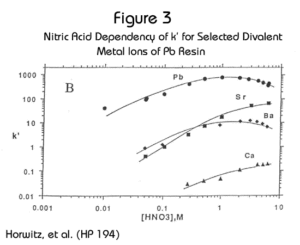
Eichrom’s Pb Resin is an extraction chromatographic material based on the same crown ether extractant used in the Sr Resin (Figure 1). Pb Resin contains at a lower concentration of the crown ether dissolved in a longer chain alcohol diluent to facilitate the stripping of Pb from the resin. Figure 2 shows the uptake of Pb2+, Na+, K+ and Tl+ on Pb Resin. Figure 3 shows Pb together with representative alkali earth metal cations. The retention of Pb is high (i.e., k’ > 100) across the range of nitric acid concentrations from 0.1M to 10M, and Pb can be eluted from the column using 6-9M HCl, 0.1M ammonium citrate, 0.05M ammonium acetate or other buffer solution. In some cases the elution of Pb from Pb Resin with deionized water may be possible. However, to ensure consistently high Pb recoveries, the use of a water eluent is not recommended.
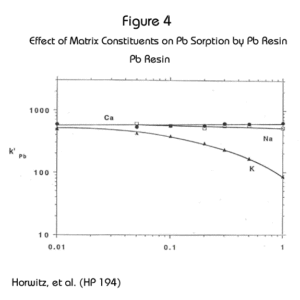
The effect of matrix constituents on lead uptake by the Pb Resin is similar to that for strontium on the Sr Resin. In Figure 4 it can be seen that calcium and sodium have little or no effect on Pb uptake even at concentrations up to 1M. Potassium does reduce Pb uptake as its concentration increases. Fortunately the retention of Pb on the Pb Resin is sufficiently high that methods can accommodate up to 1M potassium before the k’ of Pb drops below 100.
While the uptake of Pb on Pb Resin is maximized in nitric acid, it is possible to load Pb on the resin from HCl. 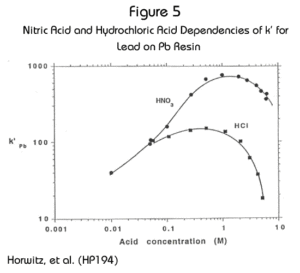 Figure 5 shows a comparison of the uptake curves for Pb from nitric and hydrochloric acid. Above 0.1M there is a divergence in the curves, with the nitric acid curve heading higher. There is still adequate retention from HCl at concentrations up to 1M. Above this HCl concentration, the retention of Pb drops off steeply. Vajda, et al. (VN195)published an HCl uptake curve for Pb on Sr Resin that corresponds to this behavior. Vajda reported a method for the separation of lead and polonium on Sr Resin, where Pb is stripped with 6M HCl. By analogy, this should be possible with Pb Resin as well.
Figure 5 shows a comparison of the uptake curves for Pb from nitric and hydrochloric acid. Above 0.1M there is a divergence in the curves, with the nitric acid curve heading higher. There is still adequate retention from HCl at concentrations up to 1M. Above this HCl concentration, the retention of Pb drops off steeply. Vajda, et al. (VN195)published an HCl uptake curve for Pb on Sr Resin that corresponds to this behavior. Vajda reported a method for the separation of lead and polonium on Sr Resin, where Pb is stripped with 6M HCl. By analogy, this should be possible with Pb Resin as well.
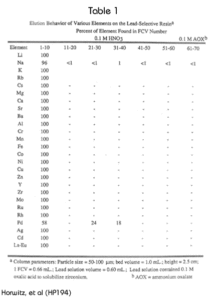 The elution behavior of various elements on the Pb Resin from 0.1M HNO3 is shown in Table 1. With the exception of Pd, all elements tested eluted quantitatively in the first 10 free column volumes.
The elution behavior of various elements on the Pb Resin from 0.1M HNO3 is shown in Table 1. With the exception of Pd, all elements tested eluted quantitatively in the first 10 free column volumes.
Pb Resin is manufactured in three particle sizes (20-50 µm, 50-100 µm, and 100-150 µm) and is sold in bottles or ready to use in prepackaged columns (for gravity flow) and cartridges (for vacuum assisted flow.) Click here for part numbers and descriptions.
1) Horwitz, E.P.; Gale, N.H.; et al, A Lead-Selective Extraction Chromatographic Resin and Its Application to the Isolation of Lead from Geological Samples, Analytica Chimica Acta, Vol. 292, pp. 263-273(1994).
2) Vajda, N., LaRosa, J., Zeisler, R., Danesi, P., Kis-Benedek, G., A novel technique for the simultaneous determination of 210Pb and 210Po using a crown ether, Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 37(3), 355-372 (1997).
3) Miura, T., Hayano, K., Nakayama, K. Determination of 210Pb and 210Po in Environmental Samples by Alpha Ray Spectometry Using and Extraction Chromatographic Resin, Analytical Sciences, 15, 23-28 (1999).